1. Steep gradient
2. Gentle gradient
3. Convex slope
4. Concave slope
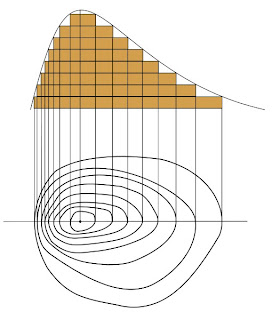
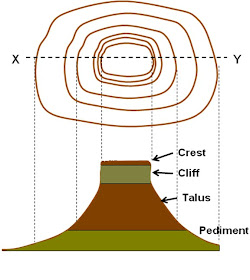
5. Conical hill
6. Butte
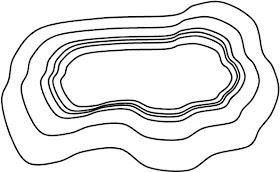
7. Mesa
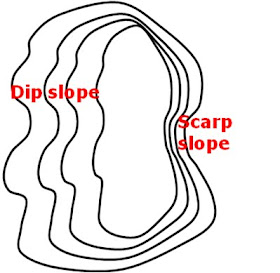
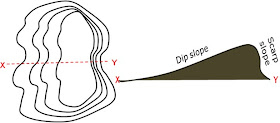
8. Dip slope
9. Scarp slope
10. Homoclinal ridge
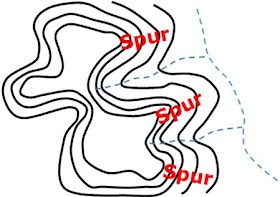
11. Valley
12. Spur
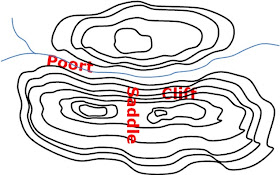
13. Poort
14. Cliff
15. Saddle/ col
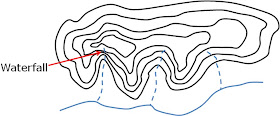
16. Waterfall
17. River channel characteristics
18. Braided stream
19. Drainage patterns
20. Superimposed drainage
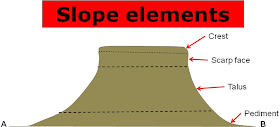
21. Slope elements
1. Types of towns
1.1. Mining town
1.2. Central place town
1.3. Tourist town
2. Rural settlements patterns
2.1. Isolated
2.2. Nucleated
3. Farming methods
3.1. Commercial
3.2. Subsistence
4. Farming techniques
4.1. Intensive
4.2. Extensive
4.3. Fruit
5. Land use zones
5.1. CBD
5.2. Industrial
5.3. Residential – high/ low income
5.4. Rural-urban fringe
6. Informal settlements
7. Tourist destinations
8. Choice of site
1. North/south facing slopes
2. Valley inversion / pollution dome
3. Anabatic/ katabatic winds
4. Erosion
5. Droughts / seasonal rainfall
6. Type of rainfall
1. Steep gradient
· Steeper terrain will have closely spaced contour lines.
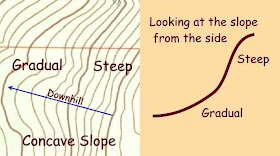
Flatter areas will have more widely spread contour lines.
· Contour lines close together at foot of hill
· Contour lines far apart near the crest (top)
· Contour lines close together at top of hill
· Contour lines far apart near the foot of the hill
5. Conical hill
· Circular shape contour lines
· Small crest
· Circular shape contour lines
· Small crest
6. Butte
· Small flat top
· Height is 2x greater than width

7. Mesa (table mountain)
· Large flat top
· 2x wider than the height
· Resistant rock layer at top – dolerite/ granite
· Small flat top
· Height is 2x greater than width

7. Mesa (table mountain)
· Large flat top
· 2x wider than the height
· Resistant rock layer at top – dolerite/ granite

8. Dip slope and 9. Scarp slope
• Dip slope = gentle slope of mountain
• Scarp slope = steep slope of mountain
10. Homoclinal ridge
· A mountain with a clear dip and scarp slope
11. Valley and 12. Spur
• Valley = contour lines bend (V) towards the top of mountain
• Usually a non-perennial stream flowing down
• Spur = contour lines bend towards the foot of mountain
• Flank on both sides of a valley
13. Poort; 14. Cliff; 15. Saddle (col)
16. Waterfall
17. Stream channel characteristics
· Turbulent flow – in upper course / steep gradient / in a valley
· Laminar flow – lower course / flat gradient
· Upper course – in valley / steep gradient / straight channel
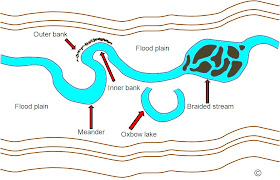
· Lower course – large meanders / oxbow lakes / large, wide floodplain / braided streams
· Outer bank – faster flowing water / more erosion / under cutting (also undercut bluff)
· Inner bank – slower flowing water / more deposition (also slip-off slope)
18. Braided stream
· Stream in lower course
· Carries large amount of stream load and sediments
· Deposition occurs due to decrease in slope and stream volume
· Deposition obstructs own flow
· Stream break up in smaller channels to flow round obstructions / sand banks or islands
 19. Drainage patterns
19. Drainage patterns
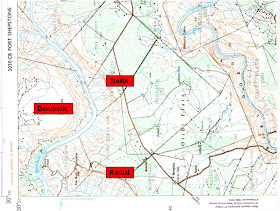
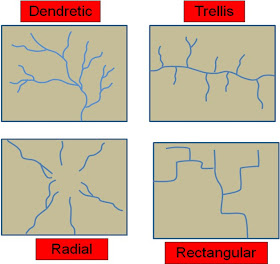
20. Superimposed drainage
• Dip slope = gentle slope of mountain
• Scarp slope = steep slope of mountain

10. Homoclinal ridge
· A mountain with a clear dip and scarp slope

11. Valley and 12. Spur
• Valley = contour lines bend (V) towards the top of mountain
• Usually a non-perennial stream flowing down
• Spur = contour lines bend towards the foot of mountain
• Flank on both sides of a valley

13. Poort; 14. Cliff; 15. Saddle (col)

16. Waterfall

17. Stream channel characteristics
· Turbulent flow – in upper course / steep gradient / in a valley
· Laminar flow – lower course / flat gradient
· Upper course – in valley / steep gradient / straight channel
· Lower course – large meanders / oxbow lakes / large, wide floodplain / braided streams
· Outer bank – faster flowing water / more erosion / under cutting (also undercut bluff)
· Inner bank – slower flowing water / more deposition (also slip-off slope)
18. Braided stream
· Stream in lower course
· Carries large amount of stream load and sediments
· Deposition occurs due to decrease in slope and stream volume
· Deposition obstructs own flow
· Stream break up in smaller channels to flow round obstructions / sand banks or islands
 19. Drainage patterns
19. Drainage patterns

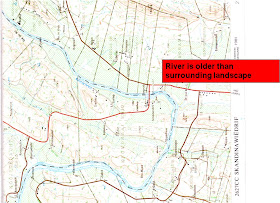
20. Superimposed drainage
The course of the river is unrelated to the present underlying geological structure
The river exposed an older underlying land structure

21. Slope elements
B. Settlements and Economic activities
1. Types of towns
· Mining towns: Town developed because of mining activities e.g. Postmasburg, Kuruman, Hotazel, Venterspos
· Central place towns: Small towns delivering services to surrounding farming community
· Tourism towns: Mostly small towns along the coast, towns where you find warm underground water
2. Rural settlements patterns
· Isolated/ dispersed settlements – farmsteads far apart / mostly in dry regions with low carrying capacity
· Nucleated settlements – farmsteads close together / small farms in wet regions with high carrying capacity
· Isolated/ dispersed settlements – farmsteads far apart / mostly in dry regions with low carrying capacity
· Nucleated settlements – farmsteads close together / small farms in wet regions with high carrying capacity
· Commercial farming – farm to produce a surplus to sell to a market / farms with names, roads, windmills, dams, canals / fire breaks / silos and mills / cut lines
· Subsistence farming – farm to produce only enough for own use / no roads, name, dams, small fragmented cultivated lands/ fields have few straight boundaries / numerous footpaths / huts
· Extensive – large farms in dry regions / low carrying capacity
· Intensive – small farms in wet regions / high carrying capacity
· CBD – where main roads converge / oldest part of town with monuments / grid street pattern
· Industrial – large buildings / outskirts of town / railway lines
· Residential – oldest and lower income have grid street pattern / newer, higher income have irregular street pattern, steep slopes, view over golf course or natural environment
· Greenbelts – areas where natural environment is kept and preserved / no development allowed / e.g. river floodplains; hills and mountains
· Recreation (Rec) – areas used for recreational purposes / e.g. sport grounds; park
· Rural urban fringe – areas surrounding build up areas (town) / here we find mixture of urban and rural functions / e.g. graveyards; golf course; sewerage works; brickworks; agricultural holdings; aerodrome; etc.
1. Aspect
- North facing slopes – receives direct sunlight / warm
- South facing slopes – in the mountain shadow / cooler
2. Valley climates
Valley breezes – anabatic wind blows during the day, up slope / katabtic wind blows at night, down slope / cold temperatures (frost pocket forms in bottom of valley
4. Pollution – industries situated in bottom of valleys / pollution trapped
5. Erosion
· Occurs along steeper slopes
· Little vegetation increase rate of erosion
· Wind breakers (trees planted in straight rows adjacent to cultivated lands) slow speed of wind down / less erosion during the dry season
6. Droughts & seasonal rainfall
· Seasonal rainfall can be identified if a topographic maps shows a lot of –
- Non-perennial streams
- Windmills
- Reservoirs
- Dams
- Canals
· Convectional rain – over interior of South Africa
· Relief / orographic rain – mountain areas
· Cyclonic rain – along the SW Cape and Southern Cape



No comments:
Post a Comment